
|
Now it is 6.5 mag (Oct. 21, Salvador Aguirre). It keeps so bright as 6-8 mag for a long time from 2011 to 2012. In the Southern Hemisphere, it will be unobservable soon. In the Northern Hemisphere, it will be extremely low from late November to late December. But after that, it will be observable in excellent condition again. It will be observable again in 2012 spring also in the Southern Hemisphere, although it locates low.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Oct. 29 17 38.66 18 43.4 1.989 1.728 60 6.6 19:58 (115, 3)
Nov. 5 17 35.33 18 50.2 2.041 1.688 55 6.6 20:07 (110, -5)
|

|
Now it is 10.0 mag (Oct. 27, Marco Goiato). It keeps 10 mag until November. It will start fading after December. But it keeps observable in excellent condition for a while in the Northern Hemisphere. It is appearing also in the Southern Hemisphere. After this, it keeps observable until 2012 spring when it fades down to 15-16 mag.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Oct. 29 6 30.78 45 3.3 1.450 2.096 116 10.4 3:30 (186, 9)
Nov. 5 6 3.65 42 13.7 1.359 2.125 128 10.5 3:10 (180, 13)
|

|
It is not observable at all due to the bad condition in this apparition.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Oct. 29 13 19.98 -4 38.4 1.993 1.067 15 11.5 3:30 (286,-14)
Nov. 5 13 49.25 -7 2.3 1.983 1.054 14 11.2 3:20 (290,-15)
|

|
It passed very near by the earth, within 0.1 A.U., and brightened up to 8.0 mag in the southern sky (Aug. 14, Willian Souza). It appeared in the morning sky in the Northern Hemisphere. It brightened up to 6.6 mag in late September (Sept. 25, Juan Jose Gonzalez). Now it is fading, but still bright as 10.2 mag (Oct. 29, Todd Augustyniak). It keeps observable while fading gradually after this. In the Southern Hemisphere, it is not observable until winter when it becomes fainter than 16 mag.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Oct. 29 11 57.47 2 9.5 1.352 0.810 36 11.3 3:30 (268, -1)
Nov. 5 12 16.60 0 30.0 1.445 0.910 38 12.2 3:20 (270, -1)
|

|
Now it is very bright as 10.8 mag (Oct. 27, Marco Goiato). It will be observable in good condition at 11-12 mag in autumn and winter.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Oct. 29 23 35.98 0 57.7 1.244 2.103 139 11.9 21:06 (180, 54)
Nov. 5 23 37.08 0 27.0 1.282 2.087 132 11.9 20:40 (180, 55)
|

|
It has brightened faster than expected, and reached up to 8.1 mag in mid August (Aug. 19, Michael Mattiazzo). However, the nucleus has been disintegrated, and it faded out and got diffuse very rapidly. The necleus has been already fainter than 22.5 mag and unable to be detected (Oct. 23, Jakub Cerny). But the remnant of the comet is still visible westwards from the predicted position, extremely large, diffuse and elongated as 40x5 arcmin. Juan Jose Gonzalez reported the total magnitude of the remnant as 10.2 mag on Oct. 21 visually.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Oct. 29 6 16.80 30 54.8 0.284 1.166 121 12.1 3:30 (185, 24)
Nov. 5 5 11.23 29 46.2 0.350 1.286 142 12.9 2:19 (180, 25)
|

|
Now it is so bright as 12.3 mag (Oct. 19, Hidetaka Sato). The condition of this apparition is bad. In the Northern Hemisphere, it is only observable from December to February in the evening very low sky after the perihelion passage. In the Southern Hemisphere, it keeps observable for a long time, although it keeps locating extremely low. The component B was not detected, fainter than 20 mag, on May 14 (Hidetaka Sato).
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Oct. 29 16 27.17 -25 43.5 1.600 0.959 34 12.2 19:58 ( 69, 15)
Nov. 5 17 4.58 -27 46.3 1.595 0.984 35 12.3 20:07 ( 67, 16)
|

|
New comet discovered in the spacecraft images. It was observed so bright as 9.4 mag (Sept. 22, Chris Wyatt). In the Southern Hemisphere, it must have located high and been observable in excellent condition from spring to summer. Now it is not observable. In the Northern Hemisphere, it will appear in the morning sky at 15 mag in late November, then it will be observable while fading gradually. In the Southern Hemisphere, further observations are very hard.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Oct. 29 14 24.67 -1 46.4 2.221 1.265 11 12.8 19:58 ( 70,-24)
Nov. 5 14 26.25 -0 4.0 2.248 1.320 15 13.2 3:20 (290,-26)
|

|
Now it is bright as 13.9 mag (Oct. 19, Hidetaka Sato). It will be unobservable in early November also in the Southern Hemisphere. It will brighten up to 11-12 mag in winter, however, it is not observable around the perihelion passage. In the Northern Hemisphere, it is not observable until 2012 summer, when it will be fainter than 15 mag.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Oct. 29 16 18.33 -32 7.5 2.526 1.801 34 13.3 19:58 ( 62, 16)
Nov. 5 16 38.39 -31 6.1 2.505 1.738 31 13.1 20:07 ( 61, 13)
|

|
It brightened rapidly and reached up to 12.9 mag (Oct. 8, Seiichi Yoshida). It keeps the current brightness until December. Then it starts fading, but it keeps observable in good condition until May when it becomes fainter than 18 mag. It locates somewhat low in the Southern Hemisphere.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Oct. 29 9 28.61 7 47.0 1.353 1.428 73 13.3 3:30 (240, 24)
Nov. 5 9 49.08 7 39.0 1.321 1.436 75 13.2 3:20 (241, 24)
|

|
Now it is bright as 14.1 mag (Oct. 3, Hidetaka Sato). It keeps bright as 13-14 mag for a long time after this until 2013. It is not observable in the Northern Hemisphere, but it is observable in good condition in the Southern Hemisphere.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Oct. 29 12 36.69 -80 17.2 5.770 5.475 67 13.5 3:30 (349, 33)
Nov. 5 12 49.45 -81 27.1 5.782 5.471 66 13.5 3:20 (350, 33)
|

|
Now it is 14.3 mag (Sept. 13, Artyom Novichonok and Vladimir Gerke). It was observed much brighter visually around 10-12 mag. It keeps the current brightness from 2011 summer to 2012 summer. But it is not observable around the perihelion. It is already too low to observe in the Southern Hemisphere. It will be unobservable also in the Northern Hemisphere in November.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Oct. 29 16 4.09 -4 27.1 3.224 2.406 29 13.8 19:58 ( 83, -2)
Nov. 5 16 18.59 -5 49.7 3.237 2.390 26 13.7 20:07 ( 79, -6)
|

|
It brightened up to 17.1 mag in late June (June 24, J. F. Hernandez). It will brighten up to 13 mag in winter. But the condition of this apparition is bad, and it will not be observable around the perihelion passage. It will appear in the morning sky at 14 mag in 2012 April in the Southern Hemisphere. It will not be observable until 2012 June in the Northern Hemisphere, when the comet will be 15.5 mag.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Oct. 29 15 12.13 -17 53.2 2.570 1.634 15 14.0 19:58 ( 65, -4)
Nov. 5 15 32.30 -19 33.7 2.564 1.616 13 13.9 20:07 ( 61, -6)
|

|
Appearing in the morning sky. Now it is bright as 14.2 mag (Oct. 24, Jean-Francois Soulier).
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Oct. 29 12 8.72 -7 39.7 7.097 6.262 30 14.2 3:30 (278, 2)
Nov. 5 12 12.99 -8 13.7 7.034 6.262 36 14.2 3:20 (277, 5)
|
|
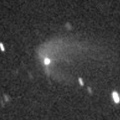
Big asteroid discovered in 1906. It suddenly showed the cometary activity on Dec. 11, probably due to an impact of a small object. It was very bright as 11.5 mag visually (Dec. 17, Juan Jose Gonzalez). It had a dust coma still on Jan. 9 (Joseph Brimacombe). Then it turned to be stellar at 13.8 mag (Apr. 5, Juan Jose Gonzalez). Now it is not observable.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Oct. 29 13 25.00 0 55.4 3.522 2.597 18 14.2 3:30 (282,-18)
Nov. 5 13 36.55 -0 21.1 3.485 2.588 21 14.2 3:20 (282,-16)
|

|
Now it is 14.3 mag and visible visually (Oct. 1, Jakub Cerny). It will be observable at 13-14 mag for a long time from 2011 to 2012. However, it will be unobservable temporarily from November to January.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Oct. 29 17 54.50 -12 28.0 5.809 5.291 54 14.2 19:58 ( 92, 25)
Nov. 5 17 54.73 -12 44.9 5.897 5.279 47 14.3 20:07 ( 87, 18)
|

|
First return of a new periodic comet which brightened up to 13 mag in a major outburst in 2005. In this apparition, it brightened up to 12 mag in 2011 summer and autumn. It will be fading after this, but it is still bright as 12.2 mag (Oct. 16, Uwe Pilz). It keeps observable in good condition until February when it fades out down to 17-18 mag. The fragment B is also observed at 20 mag. Another fragments C and D are also observed at 21-22 mag.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Oct. 29 22 39.72 4 4.0 1.591 2.329 127 14.5 20:10 (180, 51)
Nov. 5 22 42.68 4 10.6 1.679 2.349 121 14.8 20:07 (172, 50)
|

|
Now it is 13.9 mag and visible visually (Oct. 21, Jakub Cerny). It will reach up to 10 mag from January to March, but it will be too low to observe. It will be getting lower in the evening sky. In the Northern Hemisphere, it keeps observable until December when it brightens up to 12 mag. In the Southern Hemisphere, it will be unobservable soon.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Oct. 29 16 59.95 0 42.4 2.294 1.725 44 14.9 19:58 ( 95, 7)
Nov. 5 17 15.73 -0 11.6 2.264 1.661 41 14.5 20:07 ( 92, 3)
|

|
Now it is visible visually at 13.8 mag (Oct. 21, Jakub Cerny). It is expected to be 13 mag and will be observable in good condition in 2013. In the Northern Hemisphere, it keeps observable for a long time after this. It is not observable in the Southern Hemisphere.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Oct. 29 23 40.78 63 31.0 6.515 7.108 123 14.8 21:10 (180, -9)
Nov. 5 23 30.39 62 31.4 6.498 7.082 122 14.8 20:32 (180, -8)
|

|
It was expected to keep 14-15 mag for a long time from 2011 summer to 2012 summer. However, it is lost. It was observed only during two days in 2010 June. So the orbital elements are extremely uncertain. The condition is good in the Southern Hemisphere. But in the Northern Hemisphere, it is not observable until 2012 August.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Oct. 29 16 18.02 -59 20.7 3.061 2.568 51 15.0 19:58 ( 35, 29)
Nov. 5 16 30.40 -60 36.5 3.064 2.534 49 15.0 20:07 ( 33, 26)
|

|
Now it is 16.6 mag (Oct. 12, Hidetaka Sato). It is already unobservable in the Northern Hemisphere. It will be unobservable soon also in the Southern Hemisphere.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Oct. 29 15 56.92 -25 31.0 2.446 1.633 27 15.2 19:58 ( 65, 9)
Nov. 5 16 19.23 -26 9.8 2.450 1.616 25 15.1 20:07 ( 63, 7)
|
|
Now it is 15.7 mag (Oct. 20, Catalina Sky Survey). It is expected to be observable at 13 mag for a long time from 2012 summer to 2013 summer. It will be observable in excellent condition in the Southern Hemisphere. But it is not observable at brightest time in the Northern Hemisphere. It keeps observable for a while at 16 mag while brightening gradually.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Oct. 29 2 16.91 -28 54.4 3.608 4.396 137 15.7 23:46 (180, 84)
Nov. 5 2 7.89 -30 18.4 3.593 4.337 133 15.6 23:09 (180, 85)
|

|
Extremely diffuse and hardly detected by CCD images. The nucleus is already fainter than 18 mag (Oct. 15, Jean-Francois Soulier). The comet can be already disintegrated. However, Juan Jose Gonzalez reported it so bright as 9.5 mag visually on Sept. 25. In the Northern Hemisphere, it keeps locating higher than 20 degree from November to December. In the Southern Hemisphere, it will be observable in early November, then it will be getting higher rapidly.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Oct. 29 11 40.38 -1 38.2 1.879 1.272 39 15.7 3:30 (269, 4)
Nov. 5 11 44.69 -6 15.1 1.889 1.356 43 15.9 3:20 (271, 10)
|

|
It was revealed to be a comet when appearing in the morning sky in early August. It has already passed the perihelion in April, and it will be fading after this. But it is still visible visually at 14.8 mag (Oct. 2, Jakub Cerny). In the Northern Hemisphere, it keeps observable in excellent condition for a long time until 2012 summer. It is not observable at all in the Southern Hemisphere.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Oct. 29 10 56.42 47 42.9 2.768 2.683 74 15.7 3:30 (223,-16)
Nov. 5 11 9.15 47 48.7 2.752 2.734 78 15.8 3:20 (222,-16)
|

|
It brightened rapidly. Now it is bright and visible visually at 14.6 mag (Sept. 30, Sandor Szabo). It will be fading slowly after this. It keeps observable until winter when it fades out down to 17-18 mag.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Oct. 29 20 54.77 -27 16.1 2.028 2.310 93 15.7 19:58 (105, 69)
Nov. 5 21 4.69 -26 42.8 2.113 2.315 88 15.9 20:07 (100, 63)
|

|
It is expected to be bright as 9 mag from 2012 to 2013. Now it is 15.8 mag (Oct. 22, Erik Bryssinck). It is already visible visually at 14.6 mag (Oct. 1, Jakub Cerny). In the Northern Hemisphere, although it becomes low temporarily in 2011 autumn, it keeps observable in good condition for a long time until 2012 autumn when the comet brightens up to 10 mag. In the Southern Hemisphere, it is hardly observble before the perihelion passage. But it becomes observable in good condition since 2013 after the perihelion passage.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Oct. 29 13 38.76 44 57.6 5.576 5.129 58 15.8 3:30 (238,-41)
Nov. 5 13 47.42 44 32.0 5.473 5.068 61 15.7 3:20 (238,-39)
|

|
Bright new comet. Now it is 16.1 mag (Oct. 19, Hidetaka Sato). It keeps 16 mag from October to November, but it will be fainter than 18 mag in winter. In the Northern Hemisphere, it keeps locating the same altitude in the morning sky. In the Southern Hemisphere, it locates extremely low now, but it will be getting higher gradually. Juan Jose Gonzalez reported that it was visible as a 11.3-mag diffuse comet visually on Oct. 9. The orbital elements are similar to P/2006 T1 (Levy), but they seem to be different objects.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Oct. 29 11 1.17 2 31.0 1.463 1.116 49 15.8 3:30 (260, 10)
Nov. 5 11 25.07 -1 54.9 1.479 1.125 49 15.9 3:20 (264, 11)
|

|
It was very bright and visible visually as 12.4 mag in July and early August (Aug. 2, Jakub Koukal). Now it is fading rapidly. It has already faded down to 17.0 mag (Oct. 11, Artyom Novichonok and Vladimir Gerke). In the Northern Hemisphere, it keeps observable until the end of 2011 when it becomes fainter than 18 mag. It will never be observable again in the Southern Hemisphere.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Oct. 29 17 35.74 35 3.9 2.316 2.157 68 16.0 19:58 (128, -8)
Nov. 5 17 39.66 35 35.4 2.392 2.196 66 16.2 20:07 (124,-13)
|

|
It became bright as 12 mag in 2010. Now it is fading. It has already faded down to 17.1 mag (Oct. 26, S. Shurpakov).
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Oct. 29 1 49.14 1 37.7 2.920 3.895 167 16.2 23:19 (180, 53)
Nov. 5 1 44.30 1 25.3 2.964 3.913 160 16.3 22:46 (180, 54)
|

|
Now it is 16.9 mag (Oct. 13, P. Dupouy). It will be fading very slowly after this. In the Northern Hemisphere, it keeps observable for a long time until 2012 spring when it fades down to 17-18 mag. It will not be observable in the Southern Hemisphere.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Oct. 29 22 26.39 43 47.4 4.888 5.497 123 16.3 19:58 (180, 11)
Nov. 5 22 27.65 42 29.2 4.960 5.528 120 16.4 20:07 (173, 12)
|

|
It reached up to 14 mag in 2010 autumn and winter. Now it is fading. It has already faded down to 16.6 mag (Sept. 14, Hidetaka Sato). In the Southern Hemisphere, it keeps observable in good condition while fading gradually. In the Northern Hemisphere, it will never be observable again.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Oct. 29 5 59.73 -74 44.0 3.861 3.908 85 16.6 3:30 ( 0, 50)
Nov. 5 5 35.04 -76 59.7 3.929 3.951 84 16.6 2:41 ( 0, 48)
|

|
It was bright as 13.5 mag and visible visually still in 2011 summer. But it is fading now. It has already faded down to 16.2 mag (Oct. 16, P. Dupouy). It will be fainter than 18 mag in December.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Oct. 29 21 54.78 -33 8.1 3.430 3.786 103 16.7 19:58 (103, 83)
Nov. 5 21 52.99 -33 42.4 3.600 3.836 96 16.9 20:07 ( 90, 75)
|

|
Although it has passed the perihelion in last November, it is uxexpectedly bright as 16.5 mag still now (Oct. 25, C. Bell). It keeps observable in excellent condition until winter. It will keep 16-17 mag for a while after this.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Oct. 29 7 12.80 0 45.5 4.110 4.461 104 16.7 3:30 (211, 50)
Nov. 5 7 8.65 1 9.5 4.044 4.510 111 16.8 3:20 (202, 52)
|

|
It brightened up to 14.0 mag and became visible visually in August (Aug. 1, Juan Jose Gonzalez). Now it is fading. It has already faded down to 16.5 mag (Oct. 15, F. Garcia).
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Oct. 29 22 56.81 -18 6.8 1.603 2.298 122 16.8 20:27 (180, 73)
Nov. 5 23 0.19 -17 15.0 1.693 2.318 117 17.0 20:07 (177, 72)
|

|
Now it is 17.0 mag (Oct. 16, Catalina Sky Survey). It keeps observable at 17 mag for a long time from 2011 to 2012.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Oct. 29 23 50.24 14 43.3 7.224 8.065 145 16.9 21:20 (180, 40)
Nov. 5 23 45.70 14 10.0 7.303 8.070 138 16.9 20:48 (180, 41)
|
|
Now it is 17.3 mag (Oct. 19, Hidetaka Sato). It tends to be brightest after the perihelion passage. In the Northern Hemisphere, it keeps observable at 17 mag in good condition from autumn to winter. In the Southern Hemisphere, it locates low and will be hard to observe.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Oct. 29 10 13.32 20 15.5 2.353 2.173 67 17.1 3:30 (238, 8)
Nov. 5 10 24.73 20 5.2 2.312 2.212 71 17.1 3:20 (238, 9)
|

|
It brightened up to 13-14 mag and became visible visually from 2007 to 2009. Now it is fading. But it is still bright as 16.4 mag (Oct. 9, Artyom Novichonok and Vladimir Gerke). In the Northern Hemisphere, it keeps observable in excellent condition until early summer in 2012. In the Southern Hemisphere, it locates extremely low only.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Oct. 29 10 56.69 35 23.2 11.188 10.837 66 17.1 3:30 (233, -9)
Nov. 5 10 57.26 35 31.1 11.121 10.873 73 17.1 3:20 (231, -6)
|
|
Now it is 17.0 mag (Oct. 18, Toshiyuki Takahashi). It will be observable in good condition for a while. But it will be fainter than 18 mag in December.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Oct. 29 23 15.80 -10 25.4 1.260 2.049 130 17.2 20:46 (180, 65)
Nov. 5 23 18.80 -10 9.7 1.315 2.045 124 17.3 20:22 (180, 65)
|
|
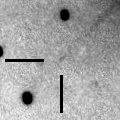
Now it is 17.2 mag (Oct. 7, IAA-AI Atacama). It keeps 17-18 mag until early 2013. It keeps observable in good condition until early 2012 in the Southern Hemisphere, although it locates low in the Northern Hemisphere. In the Northern Hemisphere, it will be observable in good condition from 2012 autumn to early 2013.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Oct. 29 0 34.36 -45 25.2 2.688 3.267 117 17.3 22:04 ( 0, 80)
Nov. 5 0 30.37 -44 21.3 2.718 3.243 113 17.3 21:33 ( 0, 81)
|

|
First return of a new comet which brightened up to 9.5 mag in a major outburst in 2006. It will approach to the earth down to 0.2 A.U. in January, and will be observable in excellent condition. However, the brightness will be quite uncertain. The comet has not been recovered yet. It was fainter than 20 mag on Oct. 2 (Jean-Francois Soulier).
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Oct. 29 22 38.91 43 5.6 0.590 1.421 125 18.5 20:09 (180, 12)
Nov. 5 22 30.56 41 48.1 0.553 1.362 121 17.4 20:07 (174, 13)
|
|
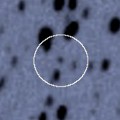
Now it is 18.6 mag (Sept. 3, Jean-Francois Soulier). It keeps observable in good condition at 17-18 mag until March. It locates low in the Southern Hemisphere.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Oct. 29 4 27.56 40 8.6 1.420 2.271 139 17.7 2:02 (180, 15)
Nov. 5 4 11.36 40 4.5 1.340 2.244 148 17.5 1:18 (180, 15)
|
|
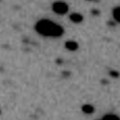
Now it is 17.8 mag (Oct. 22, C. Bell). It keeps observable at 18 mag for a long time until 2013.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Oct. 29 5 44.82 26 6.3 3.236 3.931 128 17.6 3:18 (180, 29)
Nov. 5 5 43.45 26 10.2 3.158 3.929 135 17.5 2:49 (180, 29)
|

|
Peculiar asteroid moving along a cometary orbit. Now it is 17.5 mag (Aug. 1, Siding Spring Survey)�$B!#�(BIt is observable at 17-18 mag in good condition from September to November.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Oct. 29 2 45.21 6 22.5 1.873 2.855 169 17.6 0:19 (180, 49)
Nov. 5 2 38.74 5 39.3 1.926 2.908 170 17.7 23:40 (180, 49)
|

|
Now it is 17.8 mag (Oct. 21, C. Bell). It will be observable in good condition at 18 mag from autumn to winter.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Oct. 29 3 21.06 -12 11.8 3.158 4.044 149 17.6 0:55 (180, 67)
Nov. 5 3 17.55 -13 3.4 3.149 4.038 149 17.6 0:24 (180, 68)
|
|
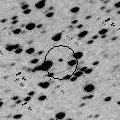
Peculiar asteroid moving along a cometary orbit. Now it is 18.4 mag (Oct. 26, Hidetaka Sato). It keeps observable at 18 mag for a long time from 2008 to 2014.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Oct. 29 8 16.27 7 23.2 6.493 6.576 90 17.7 3:30 (225, 36)
Nov. 5 8 15.54 7 41.4 6.378 6.582 97 17.7 3:20 (220, 39)
|
|
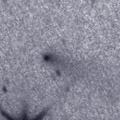
Although the condition is bad in this apparition, it brightened up to 12.8 mag in last winter (Dec. 24, Ken-ichi Kadota). Now it is fading, but it is still bright as 16.9 mag (Oct. 14, P. Dupouy). It can be observable at 17-18 mag for some more time.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Oct. 29 23 28.62 -17 44.0 2.135 2.869 129 19.1 20:59 (180, 73)
Nov. 5 23 27.48 -17 10.0 2.249 2.907 122 19.2 20:30 (180, 72)
|
|
![]()
 45P/Honda-Mrkos-Pajdusakova
45P/Honda-Mrkos-Pajdusakova 78P/Gehrels 2
78P/Gehrels 2 C/2010 X1 ( Elenin )
C/2010 X1 ( Elenin ) 73P/Schwassmann-Wachmann 3
73P/Schwassmann-Wachmann 3 C/2011 Q4 ( SWAN )
C/2011 Q4 ( SWAN ) C/2011 Q2 ( McNaught )
C/2011 Q2 ( McNaught ) 49P/Arend-Rigaux
49P/Arend-Rigaux C/2009 F4 ( McNaught )
C/2009 F4 ( McNaught ) C/2011 A3 ( Gibbs )
C/2011 A3 ( Gibbs ) 71P/Clark
71P/Clark 29P/Schwassmann-Wachmann 1
29P/Schwassmann-Wachmann 1 (596) Scheila
(596) Scheila C/2006 S3 ( LONEOS )
C/2006 S3 ( LONEOS ) 213P/2009 B3 ( Van Ness )
213P/2009 B3 ( Van Ness ) 21P/Giacobini-Zinner
21P/Giacobini-Zinner C/2010 S1 ( LINEAR )
C/2010 S1 ( LINEAR ) C/2010 M1 ( Gibbs )
C/2010 M1 ( Gibbs ) 37P/Forbes
37P/Forbes C/2011 R1 ( McNaught )
C/2011 R1 ( McNaught ) C/2011 M1 ( LINEAR )
C/2011 M1 ( LINEAR ) P/2010 JC81 ( WISE )
P/2010 JC81 ( WISE ) 48P/Johnson
48P/Johnson C/2011 F1 ( LINEAR )
C/2011 F1 ( LINEAR ) C/2011 S2
C/2011 S2 C/2011 L3 ( McNaught )
C/2011 L3 ( McNaught ) 65P/Gunn
65P/Gunn C/2008 FK75 ( Lemmon-Siding Spring )
C/2008 FK75 ( Lemmon-Siding Spring ) C/2010 B1 ( Cardinal )
C/2010 B1 ( Cardinal ) C/2009 Y1 ( Catalina )
C/2009 Y1 ( Catalina ) C/2010 FB87 ( WISE-Garradd )
C/2010 FB87 ( WISE-Garradd ) 130P/McNaught-Hughes
130P/McNaught-Hughes C/2008 S3 ( Boattini )
C/2008 S3 ( Boattini ) 164P/Christensen
164P/Christensen C/2005 L3 ( McNaught )
C/2005 L3 ( McNaught ) 253P/2011 R2 ( PanSTARRS )
253P/2011 R2 ( PanSTARRS ) P/2011 N1 ( ASH )
P/2011 N1 ( ASH ) P/2006 T1 ( Levy )
P/2006 T1 ( Levy ) (3200) Phaethon
(3200) Phaethon 244P/2010 Q1 ( Scotti )
244P/2010 Q1 ( Scotti ) 2000 EJ37
2000 EJ37 242P/2010 P3 ( Spahr )
242P/2010 P3 ( Spahr ) 2008 YB3
2008 YB3 9P/Tempel 1
9P/Tempel 1![]()










































