
|
Brightening very rapidly. It is already so bright as 6.0 mag (Dec. 14, Marco Goiato). It will approach to the earth in December and January, and it is expected to brighten up to 5 mag. In the Southern Hemisphere, it keeps observable in excellent condition until late January. In the Northern Hemisphere, it keeps extremely low until mid December. But after that, it will be observable in excellent condition.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Dec. 13 6 58.13 -41 14.7 0.796 1.477 111 7.0 1:34 ( 0, 84)
Dec. 20 6 23.13 -36 46.2 0.662 1.430 119 6.3 0:33 ( 0, 88)
|

|
It brightened up to 6.9 mag in autumn (Oct. 17, Marco Goiato). Now it is fading. But it is bright as 9.8 mag still now (Dec. 14, Marco Goiato). It is observable in excellent condition in the Southern Hemisphere. In the Northern Hemisphere, it is observable in the evening low sky in December and January.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Dec. 13 0 28.45 -41 23.8 1.767 1.975 86 9.6 20:54 ( 66, 67)
Dec. 20 0 18.12 -38 11.1 1.970 2.058 80 9.9 20:59 ( 73, 58)
|

|
The brightness evolution has slowed down before the perihelion passage, and it faded down to 11.6 mag in late October (Oct. 26, Todd Augustyniak). However, an outburst occured around Nov. 10-12, and it brightened by 2 mag. It is bright as 10.4 mag still now (Nov. 29, Seiichi Yoshida). In the Northern Hemisphere, it became unobservable temporarily in December. But it will be observable in excellent condition after January while the comet will be fading. In the Southern Hemisphere, it will keep locating extremely low after this.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Dec. 13 17 51.15 -4 41.2 2.454 1.565 19 10.4 20:54 ( 62,-27)
Dec. 20 17 53.85 -2 38.0 2.493 1.611 20 10.6 20:59 ( 58,-34)
|

|
Now it is bright as 11.7 mag (Dec. 12, Michael Mattiazzo). It will brighten up to 10 mag in January. In the Northern Hemisphere, it will be geting higher gradually. In the Southern Hemisphere, it will be getting lower gradually, and it keeps extremely low after January.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Dec. 13 20 19.66 -21 58.2 1.493 0.998 41 11.6 20:54 ( 72, 12)
Dec. 20 20 51.02 -19 25.5 1.458 0.981 42 11.0 20:59 ( 74, 11)
|

|
Now it is so bright as 10.6 mag (Nov. 29, Seiichi Yoshida). It keeps observable in the morning low sky at the same brightness for a while. In the Southern Hemisphere, it is too low to observe until December.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Dec. 13 14 11.49 -5 28.5 1.830 1.390 48 11.7 2:53 (273, 5)
Dec. 20 14 33.69 -7 5.6 1.838 1.420 49 11.9 2:54 (274, 7)
|

|
It brightened rapidly. Now it is so bright as 10.7 mag (Nov. 24, Uwe Pilz). In the Northern Hemisphere, it keeps observable in good condition until the comet will fade out in next spring. It is not observable in the Southern Hemisphere.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Dec. 13 18 49.19 55 4.6 1.529 1.676 80 11.8 20:54 (136,-41)
Dec. 20 18 59.18 51 28.7 1.631 1.696 76 12.2 20:59 (130,-44)
|

|
The brightness evolution has slowed down just before the perihelion passage. But it brightened up to 6.5 mag in September (Sept. 21, Marco Goiato). Now it is fading. It has faded down to 10.6 mag in October (Oct. 21, Chris Wyatt). It is appearing in the morning sky in the Northern Hemisphere. It will be observable in mid January also in the Southern Hemisphere. It keeps observable in good condition after this, while the comet will be fading gradually.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Dec. 13 15 58.66 -6 48.9 2.411 1.579 25 12.4 2:53 (291,-16)
Dec. 20 16 0.47 -5 39.9 2.437 1.683 31 12.7 2:54 (285,-11)
|

|
It will brighten up to 8-9 mag in 2015 spring. In the Southern Hemisphere, it will become observable in January, then it keeps observable in good condition after that. In the Northern Hemisphere, it keeps extremely low and hard to observe from December to 2015 June. It will be observable in good condition after June while the comet will be fading gradually.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Dec. 13 15 28.76 -18 2.1 2.641 1.813 26 13.0 2:53 (295, -3)
Dec. 20 15 47.94 -19 16.3 2.567 1.769 28 12.7 2:54 (294, -1)
|

|
It will brighten very rapidly, and will brighten up to 11 mag from January to February. In the Southern Hemisphere, it will be observable in the morning sky after late February while the comet will be fading. It is hardly observable in the Northern Hemisphere.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Dec. 13 16 4.69 -10 29.1 2.237 1.373 21 14.1 2:53 (294,-15)
Dec. 20 16 28.78 -12 29.5 2.197 1.339 22 13.5 2:54 (295,-13)
|

|
Now it is 14.1 mag (Nov. 17, Chris Wyatt). Getting brighter than originally expected, and it is already visible visually. It is expected to brighten up to 4 mag from autumn to winter in 2015. It is observable in good condition in the Southern Hemisphere until the highlight, or in the Northern Hemisphere after the highlight.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Dec. 13 22 22.44 -25 22.5 4.930 4.654 68 13.6 20:54 ( 83, 38)
Dec. 20 22 22.68 -25 10.5 4.971 4.582 61 13.6 20:59 ( 80, 31)
|

|
It brightened rapidly in outburst in mid October in 2013. Now it is fading. It has already faded down to 13.0 mag (Oct. 18, Con Stoitsis). In the Southern Hemisphere, it keeps observable in good condition for a long time until the comet fades out. In the Northern Hemisphere, it keeps extremely low after this.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Dec. 13 22 24.65 -43 20.9 4.192 3.875 64 13.6 20:54 ( 61, 44)
Dec. 20 22 32.30 -42 28.6 4.333 3.940 60 13.7 20:59 ( 61, 40)
|

|
Now it is 13.9 mag (Nov. 29, Seiichi Yoshida). It is fainter than originally predicted by 2 mag. In the Northern Hemisphere, it keeps observable at 14 mag in excellent condition from 2014 summer to 2015 spring. It locates somewhat low in the Southern Hemisphere.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Dec. 13 11 18.75 17 18.6 1.701 2.065 96 13.9 2:53 (227, 22)
Dec. 20 11 27.96 17 1.9 1.646 2.081 101 13.9 2:54 (223, 26)
|

|
Now it is not observable. It will appear in the morning sky again in January.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Dec. 13 16 46.22 -29 24.2 7.055 6.087 9 14.1 2:53 (315, -9)
Dec. 20 16 52.48 -29 33.4 7.033 6.085 14 14.1 2:54 (312, -5)
|

|
Now it is 14.8 mag (Sept. 16, Taras Prystavski). It is expected to brighten up to 13 mag and to be observable in good condition in 2015. It becomes unobservable temporarily from October to January.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Dec. 13 16 30.05 -12 52.5 4.554 3.615 15 14.4 2:53 (301,-18)
Dec. 20 16 40.72 -13 10.6 4.510 3.597 19 14.3 2:54 (298,-14)
|

|
Now it is 14.8 mag (Dec. 12, Mike Wolle). It will be observable at 14 mag in excellent condition in winter.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Dec. 13 23 21.93 -4 12.7 1.002 1.391 88 14.7 20:54 (116, 38)
Dec. 20 23 37.43 -1 35.8 1.020 1.372 86 14.6 20:59 (115, 33)
|

|
Now it is 14.7 mag (Nov. 28, Mt. Lemmon Survey). It keeps 15 mag until February, and it will be observable in excellent condition in the Northern Hemisphere. It locates somewhat low in the Southern Hemisphere.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Dec. 13 6 58.72 27 11.3 1.538 2.476 157 14.8 1:34 (180, 28)
Dec. 20 6 53.26 26 43.5 1.511 2.475 165 14.9 1:01 (180, 28)
|

|
Now it is 14.9 mag (Nov. 22, Ken-ichi Kadota). It keeps 15 mag for a long time from 2014 to 2015. It is observable in excellent condition in 2014 in the Southern Hemisphere, or in 2015 in the Northern Hemisphere.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Dec. 13 0 10.43 -21 33.3 3.793 3.961 92 14.9 20:54 (107, 58)
Dec. 20 0 10.12 -19 45.8 3.885 3.950 86 14.9 20:59 (102, 51)
|

|
Now it is 13.7 mag (Nov. 29, Seiichi Yoshida). It will be observable at 14 mag in excellent condition from October to December.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Dec. 13 5 14.48 36 21.1 0.818 1.791 166 14.9 23:46 (180, 19)
Dec. 20 5 8.87 37 27.5 0.847 1.812 163 15.1 23:13 (180, 17)
|

|
Now it is 18.2 mag (Nov. 17, J. Oey, P. Camilleri, H. Williams). It will brighten up to 9 mag in 2015 spring. But the condition of this apparition is bad. In the Southern Hemisphere, it keeps observable until winter when the comet will be 13 mag. But it is not observable around the brightest days. In the Northern Hemispehre, it keeps extremely low and hard to observe. It will be observable after 2015 autumn when the comet will fade out.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Dec. 13 21 35.88 -40 57.8 2.628 2.230 55 15.3 20:54 ( 61, 35)
Dec. 20 21 49.15 -39 22.0 2.636 2.179 52 15.1 20:59 ( 61, 31)
|

|
Now it is 16.1 mag (Nov. 13, J. Oey, P. Camilleri, H. Williams). The brightness evolution is somewhat slow. It keeps 15-16 mag for a long time from 2014 autumn to 2015 autumn. In the Southern Hemisphere, it keeps observable in excellent condition for a long time. In the Northern Hemisphere, it is unobservable until 2015 June.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Dec. 13 7 49.53 -71 2.9 2.110 2.206 82 15.2 2:26 ( 0, 54)
Dec. 20 6 39.99 -74 46.8 2.088 2.172 81 15.1 0:51 ( 0, 50)
|

|
It brightened up to 11-12 mag in 2012. It has already faded down to 14.9 mag (Aug. 12, Taras Prystavski). Appearing in the morning sky again. It will be observable at 15 mag in good condition again in 2015.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Dec. 13 12 9.29 -10 22.1 8.863 8.654 74 15.1 2:53 (260, 32)
Dec. 20 12 8.45 -10 28.3 8.777 8.691 81 15.1 2:54 (254, 38)
|

|
Now it is 15.5 mag (Oct. 28, Sandor Szabo). It keeps 15 mag from autumn to winter, but it is extremely diffuse. It moves southwards fast in winter.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Dec. 13 9 41.28 -14 39.8 1.422 1.936 105 15.1 2:53 (228, 62)
Dec. 20 9 40.40 -18 56.8 1.404 1.968 109 15.2 2:54 (220, 70)
|

|
Now it is 13.5 mag (Oct. 25, Seiichi Yoshida). It keeps bright as 13-14 mag for a long time from 2013 to 2014.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Dec. 13 21 31.89 -22 44.8 3.726 3.305 57 15.2 20:54 ( 80, 27)
Dec. 20 21 40.52 -21 52.7 3.819 3.317 52 15.3 20:59 ( 78, 21)
|

|
Now it is 14.0 mag and visible visually (Nov. 29, Seiichi Yoshida). It keeps observable for a long time after this while the comet will be fading gradually.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Dec. 13 10 0.73 0 49.4 1.979 2.473 108 15.2 2:53 (219, 47)
Dec. 20 10 1.39 0 26.5 1.936 2.515 115 15.3 2:54 (210, 51)
|

|
Now it is 15.4 mag (Oct. 28, Sandor Szabo). It will brighten up to 14 mag from 2015 to 2016. It is observable in good condition in the Southern Hemisphere. It locates somewhat low in the Northern Hemisphere.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Dec. 13 3 49.40 -24 8.2 4.065 4.734 127 15.3 22:20 (180, 79)
Dec. 20 3 39.15 -23 16.4 4.093 4.707 123 15.3 21:42 (180, 78)
|

|
Now it is 13.3 mag (Sept. 22, Seiichi Yoshida). It will be unobservable temporarily in winter, but it will be observable at 15-16 mag in good condition again in 2015.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Dec. 13 18 33.90 -14 10.5 8.038 7.119 19 15.3 20:54 ( 62,-13)
Dec. 20 18 36.50 -14 30.0 8.096 7.146 14 15.4 20:59 ( 57,-18)
|

|
It brightened up to 6.0 mag from July to August (July 24, Maik Meyer). Now it is fading. It has already faded down to 13.1 mag (Nov. 15, Uwe Pilz). It is already unobservable in the Southern Hemisphere. It will be unobservable in late December also in the Northern Hemisphere.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Dec. 13 19 40.66 -3 8.2 3.462 2.775 39 15.3 20:54 ( 82, -7)
Dec. 20 19 45.53 -3 15.6 3.621 2.863 34 15.6 20:59 ( 77,-12)
|

|
Now it is 14.2 mag (Oct. 4, Jakub Cerny). It keeps 13-14 mag and observable in good condition in the Northern Hemisphere for a long time from 2013 to 2014. It locates low in the Southern Hemisphere. Two fragments, B and C, are also visible at 18-20 mag.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Dec. 13 22 36.50 21 12.9 4.594 4.681 88 15.5 20:54 (127, 12)
Dec. 20 22 38.25 19 53.3 4.750 4.722 82 15.6 20:59 (121, 8)
|

|
Now it is 15.7 mag (Nov. 13, A. Klotz, F. Kugel, J. Nicolas). In the Northern Hemisphere, it keeps 15-16 mag and observable in excellent condition for a long time until early summer in 2015. In the Southern Hemisphere, it is not observable until mid January.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Dec. 13 13 2.74 32 57.6 3.534 3.551 82 15.7 2:53 (233, -5)
Dec. 20 13 10.02 32 46.8 3.469 3.561 87 15.7 2:54 (230, -1)
|

|
It will approach to the sun down to 0.3 a.u. in 2015 July, and it is expected to be bright. Now it is 16.0 mag (Nov. 15, Ken-ichi Kadota). It keeps observable while the comet will be brightening gradually until January when the comet will be 15 mag. The condition is bad after that and it will be hard to observe. But in the Southern Hemisphere, it will be observable after mid July in 2015, and keeps observable while the comet will be fading gradually. In the Northern Hemisphere, it is extremely hard to observe after 2015.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Dec. 13 22 47.80 -25 16.4 3.692 3.543 73 15.8 20:54 ( 87, 43)
Dec. 20 22 49.07 -24 18.8 3.713 3.456 67 15.7 20:59 ( 84, 36)
|

|
Now it is 15.3 mag (Nov. 27, Mt. Lemmon Survey). It will pass the perihelion on Mar. 15. In the Northern Hemispehre, it keeps observable in good condition until late February. In the Southern Hemisphere, it keeps observable until mid February, but it locates low.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Dec. 13 2 50.44 32 43.0 0.769 1.678 145 15.8 21:20 (180, 22)
Dec. 20 2 23.49 29 7.0 0.763 1.608 133 15.9 20:59 (172, 26)
|

|
Now it is 15.5 mag (Nov. 29, Catalina Sky Survey). It keeps observable at 15-16 mag for a long time from 2015 to 2016. In the Northern Hemisphere, it is observable in excellent condition. It locates somewhat low in the Southern Hemisphere.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Dec. 13 3 16.89 26 20.3 4.761 5.649 152 15.9 21:48 (180, 29)
Dec. 20 3 11.92 26 43.2 4.802 5.629 144 15.9 21:16 (180, 28)
|

|
It is bright as 14.1 mag still now (Oct. 25, Seiichi Yoshida). It will be fading after this. But it keeps observable until March when it becomes fainter than 18 mag.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Dec. 13 23 59.04 -12 12.8 2.113 2.394 94 16.2 20:54 (117, 50)
Dec. 20 0 6.93 -11 10.6 2.211 2.409 89 16.4 20:59 (112, 45)
|

|
Now it is 16.6 mag (Nov. 19, Catalina Sky Survey). It will brighten up to 16 mag and will be observable in excellent condition in winter.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Dec. 13 11 34.35 6 3.2 1.820 2.053 88 16.3 2:53 (239, 28)
Dec. 20 11 44.34 5 29.4 1.756 2.066 93 16.3 2:54 (235, 32)
|

|
First return of a new periodic comet discovered in 2004. It brightened very rapidly as expected. Now it is 15.9 mag (Nov. 26, Catalina Sky Survey). It will be observable in excellent condition from autumn to winter.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Dec. 13 0 0.50 6 16.8 0.855 1.431 101 16.3 20:54 (134, 37)
Dec. 20 0 23.71 6 47.4 0.903 1.450 100 16.4 20:59 (132, 35)
|

|
Now it is 16.2 mag (Nov. 24, Mt. Lemmon Survey). It will brighten up to 16 mag in winter, and will be observable in excellent condition.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Dec. 13 8 26.90 13 1.7 3.331 4.082 134 16.4 2:53 (183, 42)
Dec. 20 8 25.17 12 54.2 3.265 4.084 141 16.3 2:33 (180, 42)
|

|
Now it is 15.9 mag (Nov. 29, Ken-ichi Kadota). It will be higher gradually, and will be observable at 16-17 mag in good condition from winter to spring. It will be observable after January also in the Southern Hemisphere.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Dec. 13 14 27.35 -6 29.0 2.407 1.840 44 16.4 2:53 (277, 2)
Dec. 20 14 44.85 -7 28.7 2.374 1.852 47 16.4 2:54 (276, 5)
|
|
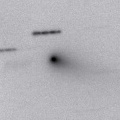
It brightened up to 13.8 mag from summer to autumn (Sept. 16, Taras Prystavski). Now it is fading rapidly. It has already faded down to 17.1 mag (Nov. 9, K. Hills). It keeps observable in good condition until February when the comet will be fainter than 18 mag.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Dec. 13 0 13.00 -3 54.1 2.249 2.617 100 16.5 20:54 (129, 47)
Dec. 20 0 19.85 -3 4.7 2.367 2.649 95 16.7 20:59 (123, 42)
|

|
Now it is 16.8 mag (Nov. 15, J. F. Hernandez). It will pass close to the earth from spring to summer in 2016, and it is expected to be observable at 6-7 mag in good condition. In the Northern Hemispehre, it keeps observable in good condition until 2015 spring when the comet will brighten up to 15.5 mag. In the Southern Hemisphere, it keeps low for a long time until 2016 spring.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Dec. 13 6 15.68 36 27.6 4.909 5.853 161 16.6 0:52 (180, 19)
Dec. 20 6 6.77 36 39.4 4.831 5.791 166 16.5 0:15 (180, 18)
|

|
Now it is 17.2 mag (Nov. 19, V. Luna). It will brighten up to 13 mag in 2016. In the Northern Hemisphere, it will be observable at 16 mag in excellent condition in this winter. It locates somewhat low in the Southern Hemisphere.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Dec. 13 6 25.49 28 6.9 2.321 3.280 164 16.9 1:01 (180, 27)
Dec. 20 6 19.28 28 15.4 2.277 3.254 171 16.8 0:27 (180, 27)
|
|
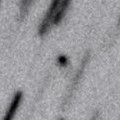
Now it is 16.8 mag (Dec. 13, K. Sarneczky). It keeps 17 mag until January, and it will be observable in excellent condition in the Northern Hemisphere.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Dec. 13 5 10.54 42 6.8 0.877 1.836 160 17.0 23:42 (180, 13)
Dec. 20 5 2.80 45 1.2 0.882 1.826 156 17.0 23:06 (180, 10)
|

|
It brightened up to 2 mag by unusual major outburst in 2007. It brightened up to 12.6 mag in this apparition (June 25, Taras Prystavski). Now it is fading. It has already faded down to 16.3 mag (Dec. 2, Yasukazu Ikari). In the Northern Hemisphere, it keeps observable until it fades out in 2015. In the Southern Hemisphere, it keeps extremely low after this.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Dec. 13 4 21.49 49 21.0 1.895 2.799 151 17.0 22:53 (180, 6)
Dec. 20 4 14.45 48 26.5 1.943 2.829 148 17.3 22:18 (180, 7)
|
|
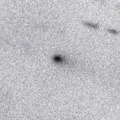
It brightened up to 14.6 mag in summer (July 8, Hidetaka Sato). Now it is fading. It has already faded down to 18.8 mag (Nov. 20, Yasukazu Ikari). It is fading much faster than predicted. The condition is good in the Northern Hemispehre. It locates somewhat low in the Southern Hemisphere.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Dec. 13 8 42.74 13 17.6 1.570 2.337 130 17.1 2:53 (188, 41)
Dec. 20 8 38.85 13 32.2 1.550 2.382 139 17.2 2:46 (180, 42)
|

|
Now it is 16.9 mag (Nov. 18, R. Ligustri). It keeps 13 mag for a long time from 2015 to 2016, and will be observable in excellent condition in the Northern Hemisphere. In the Southern Hemisphere, it is observable only until mid 2015 March.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Dec. 13 4 23.01 17 55.5 4.168 5.128 165 17.2 22:54 (180, 37)
Dec. 20 4 16.16 18 24.7 4.155 5.078 157 17.2 22:20 (180, 37)
|
|
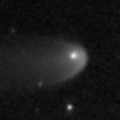
Now it is between 15.7 mag (Nov. 13, Yasukazu Ikari) and 19.1 mag (Nov. 25, A. Maury, J.-F. Soulier, J.-G. Bosch, T. Noel). Extremely diffuse, and hard to observe.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Dec. 13 3 18.64 -3 55.8 8.477 9.253 140 17.2 21:50 (180, 59)
Dec. 20 3 15.94 -3 37.8 8.583 9.289 133 17.3 21:20 (180, 59)
|

|
Now it is 18.9 mag (Nov. 20, Yasukazu Ikari). It was observed at 17 mag from 2013 to early 2014. It will be observable at 17.5 mag in good condition again from autumn to winter in 2014. But recently, it is fainter than this ephemeris.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Dec. 13 8 40.81 12 51.4 2.570 3.303 131 17.3 2:53 (188, 42)
Dec. 20 8 38.78 12 44.8 2.513 3.317 138 17.3 2:46 (180, 42)
|

|
First return of a peculiar asteroid 1998 HO121. It keeps observable at 17-18 mag from 2015 to 2016.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Dec. 13 7 23.05 6 9.6 2.482 3.342 145 17.5 1:58 (180, 49)
Dec. 20 7 20.23 6 1.6 2.418 3.320 152 17.4 1:28 (180, 49)
|

|
Now it is 17.5 mag (Nov. 29, Ken-ichi Kadota). It was observed around 17-18 mag in early 2014. It will be observable around 17-18 mag again from 2014 autumn to 2015 spring, in excellent condition in the Northern Hemisphere. It is not observable in the Southern Hemisphere.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Dec. 13 10 56.19 54 59.4 4.679 5.130 112 17.5 2:53 (202, -6)
Dec. 20 10 57.31 55 22.3 4.618 5.134 116 17.4 2:54 (198, -4)
|

|
Peculiar asteroid with a cometary orbit of 45-years period. Now it is 18.3 mag (Oct. 4, M. Jaeger, et al.). It will brighten up to 17 mag from November to December, and will be observable in excellent condition.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Dec. 13 3 42.33 7 43.7 1.887 2.795 152 17.4 22:13 (180, 47)
Dec. 20 3 24.98 5 0.8 1.983 2.812 140 17.7 21:28 (180, 50)
|
|
Now it is 17.1 mag (Nov. 22, Ken-ichi Kadota). It keeps observable at 17-18 mag from summer to winter in excellent condition in the Northern Hemisphere. It locates somewhat low in the Southern Hemisphere.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Dec. 13 7 0.00 20 6.1 1.677 2.610 156 17.5 1:35 (180, 35)
Dec. 20 6 53.98 20 36.8 1.676 2.639 165 17.6 1:02 (180, 34)
|

|
It brightened up to 12-13 mag from 2012 to 2013. Now it is fading. But it is bright as 16.9 mag still now (Nov. 24, K. Hills). It keeps 16-17 mag until autumn, and will be observable in good condition.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Dec. 13 0 15.42 -15 27.0 3.993 4.216 96 17.6 20:54 (117, 55)
Dec. 20 0 17.27 -14 42.5 4.113 4.232 90 17.7 20:59 (110, 49)
|

|
Now it is 19.6 mag (Dec. 2, A. Maury, J.-F. Soulier, J.-G. Bosch, T. Noel). Now it is around the aphelion. In the Northern Hemisphere, it is observable at 17.5 mag in good condition from winter to spring. It locates somewhat low in the Southern Hemisphere.
Date(TT) R.A. (2000) Decl. Delta r Elong. m1 Best Time(A, h)
Dec. 13 9 20.80 25 20.9 4.035 4.675 125 17.9 2:53 (196, 28)
Dec. 20 9 19.40 25 43.6 3.943 4.667 132 17.8 2:54 (188, 29)
|
|
![]()
 P/2014 X1 ( Elenin )
P/2014 X1 ( Elenin ) 17P/Holmes
17P/Holmes 16P/Brooks 2
16P/Brooks 2 C/2014 W2 ( PanSTARRS )
C/2014 W2 ( PanSTARRS ) C/2009 F4 ( McNaught )
C/2009 F4 ( McNaught ) 119P/Parker-Hartley
119P/Parker-Hartley (347449) 2012 TW236
(347449) 2012 TW236 C/2013 U2 ( Holvorcem )
C/2013 U2 ( Holvorcem ) 2013 NS11
2013 NS11 191P/McNaught
191P/McNaught 246P/2010 V2 ( NEAT )
246P/2010 V2 ( NEAT ) 65P/Gunn
65P/Gunn![]()

















































